Research progress of MXenes electrocatalysts in water splitting and metal-air batteries
Background introduction
MXenes is a new two-dimensional transition metal carbide, nitride and carbonitride, which is considered to be the next promising electrocatalytic candidate material. Compared with other two-dimensional materials, MXenes has received more and more attention due to its high conductivity 10000 S cm-1, composition diversity, thin structure, tunable surface, easy-to-adjust surface, and hydrophilicity.
MXenes are derived from their MAX precursors and have a general formula of Mn+1XnTx. M stands for transition metals Ti, V, Cr, Mo, Nb, etc., X stands for C or N, and T stands for functional groups -O,- OH and -F. A large number of stable MXenes have been predicted theoretically, and more than 30 types have been synthesized from the corresponding MAX. The tunability of the composition of MXenes is conducive to the regulation of the electronic structure. The unique two-dimensional layered structure provides a large specific surface area and maximizes the exposure of active sites. In addition, compared with carbon-based carriers, its excellent corrosion resistance and hydrophilicity expand the scope of application. The functional group greatly promotes the assembly of MXene nanosheets and interacts with other materials, which can effectively avoid the aggregation of nanomaterials and optimize the electronic structure of the MXenes-based hybrid. Based on the above, MXenes shows great promise as an electrocatalyst and supporting energy conversion.
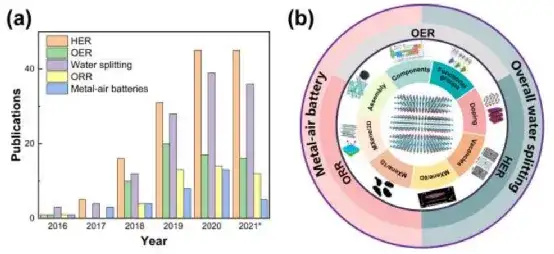
This review introduced the synthesis of MXenes, focusing on the application progress of MXenes in electrocatalysis, including HER, OER, ORR and bifunctional activity HER/OER and OER/ORR. The strategies to improve the electrocatalytic performance of MXenes and its hybrids are comprehensively discussed, including surface functional group control, defect engineering, heteroatom doping, active material loading, and hybrid nanostructure design. In addition, the challenges and prospects of MXene in electrocatalytic applications are also discussed.
MXenes is a new two-dimensional transition metal carbide, nitride and carbonitride, which is considered to be the next promising electrocatalytic candidate material. Compared with other two-dimensional materials, MXenes has received more and more attention due to its high conductivity 10000 S cm-1, composition diversity, thin structure, tunable surface, easy-to-adjust surface, and hydrophilicity.
MXenes are derived from their MAX precursors and have a general formula of Mn+1XnTx. M stands for transition metals Ti, V, Cr, Mo, Nb, etc., X stands for C or N, and T stands for functional groups -O,- OH and -F. A large number of stable MXenes have been predicted theoretically, and more than 30 types have been synthesized from the corresponding MAX. The tunability of the composition of MXenes is conducive to the regulation of the electronic structure. The unique two-dimensional layered structure provides a large specific surface area and maximizes the exposure of active sites. In addition, compared with carbon-based carriers, its excellent corrosion resistance and hydrophilicity expand the scope of application. The functional group greatly promotes the assembly of MXene nanosheets and interacts with other materials, which can effectively avoid the aggregation of nanomaterials and optimize the electronic structure of the MXenes-based hybrid. Based on the above, MXenes shows great promise as an electrocatalyst and supporting energy conversion.
This review introduced the synthesis of MXenes, focusing on the application progress of MXenes in electrocatalysis, including HER, OER, ORR and bifunctional activity HER/OER and OER/ORR. The strategies to improve the electrocatalytic performance of MXenes and its hybrids are comprehensively discussed, including surface functional group control, defect engineering, heteroatom doping, active material loading, and hybrid nanostructure design. In addition, the challenges and prospects of MXene in electrocatalytic applications are also discussed.
Original link: Research Progress of MXene-based Catalysts for ElectrochemicalWater-splitting and Metal-air Batteries
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.09.034
This information is sourced from the Internet for academic exchanges. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.09.034
This information is sourced from the Internet for academic exchanges. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately
18915694570
Previous: Yuan Quan/Sun Zhijun/T


