Liu Yang/Kang Chunsheng/Shi Linqi Biomaterials: Virus-like nanoparticle delivery system enhances CRISPR/Cas9-based cancer immunotherapy

The clustered regularly spaced short palindrome repeats related protein 9 system has broad prospects for cancer gene therapy. However, due to the complex signal network and various compensation mechanisms in tumors, the effect of regulating single molecular pathways on cancer treatment is limited. Researcher Liu Yang, Professor Shi Linqi of Nankai University and Professor Kang Chunsheng of Tianjin Medical University have jointly reported a virus-like nanoparticle as a multifunctional nano-platform to co-deliver CRISPR/Cas9 system and small molecule drugs for effective treatment Malignant tumors.
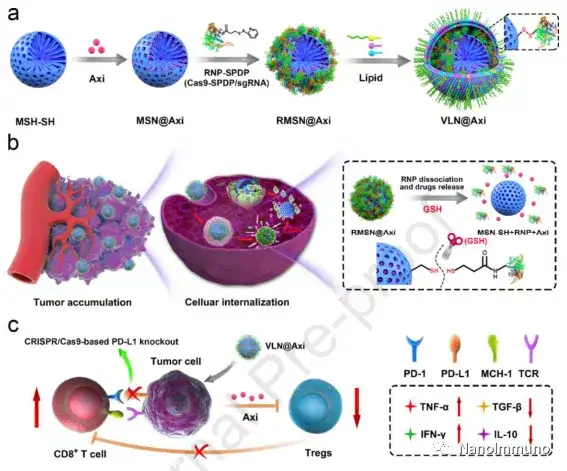
VLN has a core-shell structure in which small molecule drugs and the CRISPR/Cas9 system are loaded in a mesoporous silica nanoparticle -based core, which is further wrapped with a lipid shell. This structure makes the VLN stable during blood circulation. When reaching the tumor, the VLN releases the CRISPR/Cas9 system and small molecule drugs in response to the reducing microenvironment, resulting in the coordinated regulation of multiple cancer-related pathways. VLN can co-deliver a combination of sgRNA and small molecule drugs to tumor sites, and has shown great potential as a general platform for the development of advanced combination therapies for malignant tumors.
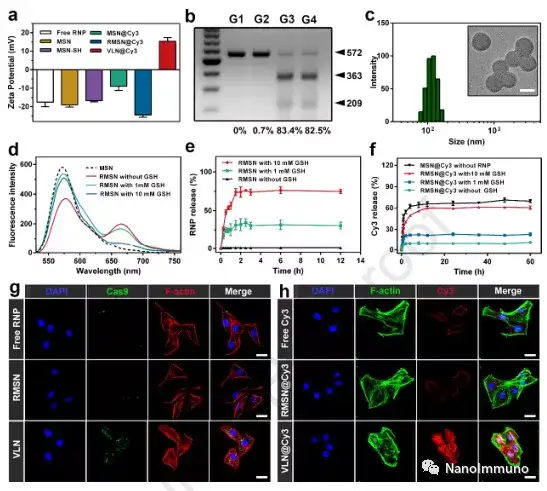
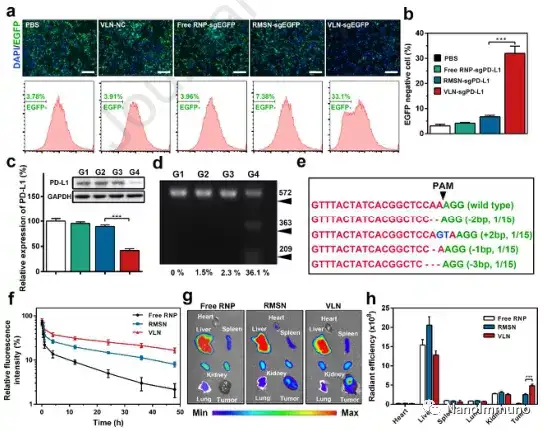
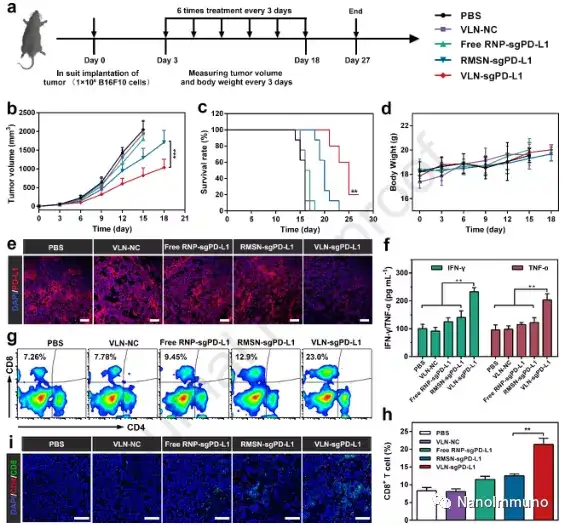
This article proves that virus-like nanoparticles are a multifunctional nano-platform that can co-deliver CRISPR/Cas9 system and small molecule drugs for effective malignant cancer treatment. VLN has a core-shell structure in which small molecule drugs and the CRISPR/Cas9 system are loaded in an MSN-based core, which is further encapsulated by a lipid layer containing PEG 2000 -DSPE. This structure can keep VLN stable during blood circulation and protect ribonucleoprotein from enzymatic degradation. When reaching the tumor, the VLN releases the CRISPR/Cas9 system and small molecule drugs in response to the reducing microenvironment, resulting in the coordinated regulation of multiple cancer-related pathways. By co-delivering tyrosine kinase inhibitor axitinib and sgRNA targeting PD-L1, VLN can activate T cells and reduce Tregs in TME, thereby enhancing the growth inhibitory effect on melanoma.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120275
This information is sourced from the Internet for academic exchanges only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately.
18915694570
Previous: Professor Jia Yunfang


