Chen Xueyuan/Lu Shan Angew: Lysozyme-photodynamic therapy strategy based on intelligent up-conversion nano-platform used to fight drug-resistant bacteria


The emergence of drug-resistant bacteria has attracted great attention from the society and promoted the exploration of advanced antibacterial methods. NIR light-triggered antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (PDT) with lanthanide-doped up-conversion nanoparticles (UCNP) as the energy donor has the advantages of high tissue penetration, broad antibacterial spectrum, and less acquired drug resistance, but Its efficacy still needs to be further improved. here,Researcher Chen Xueyuan and Associate Researcher Lu Shan, Fujian Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of SciencesA new type of bio-inorganic nano hybrid was designed, and for the first time, lysozyme (LYZ) was combined with the UCNP-PDT system to improve the efficiency of fighting drug-resistant bacteria.
The nano-platform can quickly adhere to bacteria, and realize the release of bacteria-sensitive LYZ and the synergistic LYZ-PDT effect. Therefore, it has strong bactericidal ability and significant antibacterial effect on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. This research provides a solid theoretical basis for the design of high-efficiency antibacterial nanomaterials, and provides a new collaborative strategy for combating bacterial infections in deep tissues.
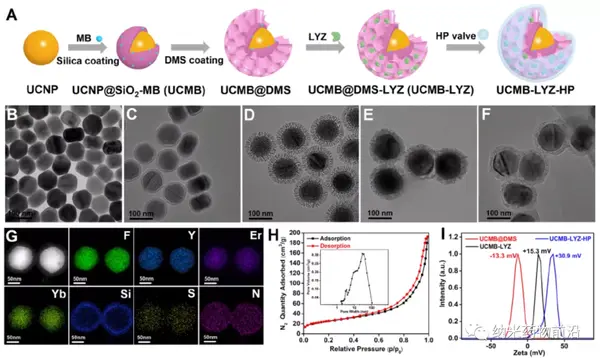
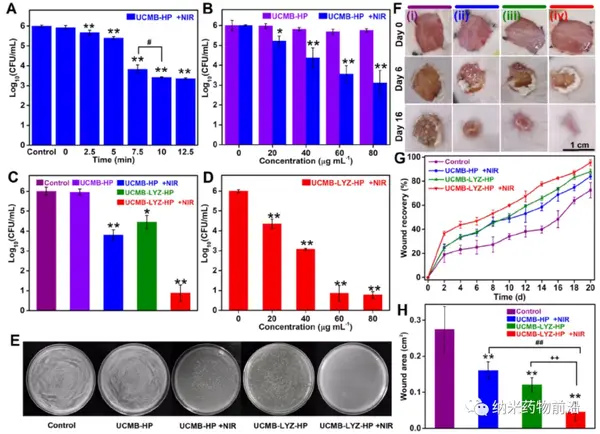
Zhuo Li. et al. Synergistic lysozyme-photodynamic therapy against resistant bacteria based on an intelligent upconversion nanoplatform. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 2021
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202103943
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202103943


Scan the QR code to follow Scan the QR code to follow us Contact: 17319402180

This information is sourced from the Internet for academic exchanges. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately
18915694570
Previous: The team of Professor


