AFM by Mei Yingwu of Zhengzhou University and Chen Yongmei of Shaanxi University of science and technology β- Dextrin hydrogel biomimetic glucose triggered insulin release system
[Abstract]
The human body starts with the specific binding of D- glucose and biological receptors, and has a fine metabolic system to regulate the D- glucose level in the blood. However, the release of insulin can induce hyperglycemia or type I diabetes. Although insulin delivery is an effective form of treatment for hyperglycemia, there is still insufficient self regulatory trigger for on-demand insulin release.
Recently, Mei Yingwu, associate professor of Basic Medical College of Zhengzhou University, Renqi Wang, doctor of Shaanxi University of science and technology, and Professor Chen Yongmei jointly proposed a bionic glucose trigger insulin release system, that is, a bidentate insulin loaded system β- Cyclodextrin based hydrogel; The dual self-regulation system displays specific D-glucose response to achieve accurate monitoring and simultaneous on-demand triggering of insulin release. D-glucose and bidentate β- The specific binding of cyclodextrins induces the release of protons, leading to the macroscopic expansion of hydrogels, and then triggering the on-demand and long-term replenishment of insulin. Conversely, the isomers of D- glucose, such as D- fructose and D- galactose, cause hydrogel contraction and delay insulin release. In vivo studies of type I diabetic mice confirm that although the teeth are double teeth β- CD hydrogel is preloaded with short acting insulin, but it can control blood sugar level within 12 hours. Related papers are entitled biological glucose trigger insulin release system based on hydrogel loading biology β- Cyclodextrin was published in advanced functional materials.
[main picture guide]
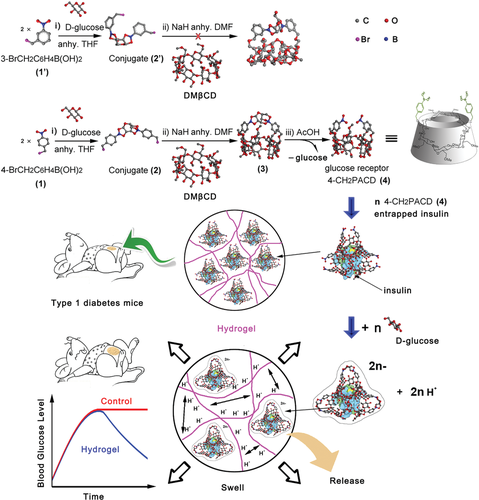
Schematic 1 is based on 2,6-o-dimethyl- β- CD (DM β CD) D-glucose receptor. i) Synthesis of D-glucose bridged ligands 2 and 2. 2) in DM β Nucleophilic substitution on CD. III) AcOH catalyzed hydrolysis of borate ester bonds and the mechanism of D- glucose responsive hydrogels swelling and insulin release.
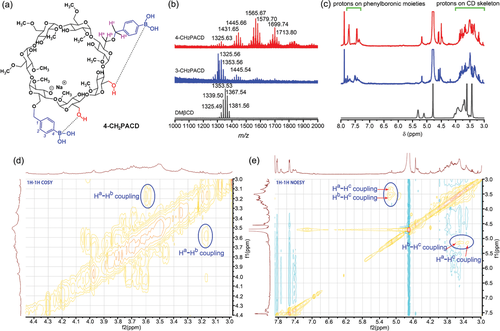
Figure 1 DM β Characterization of CD and its derivatives.
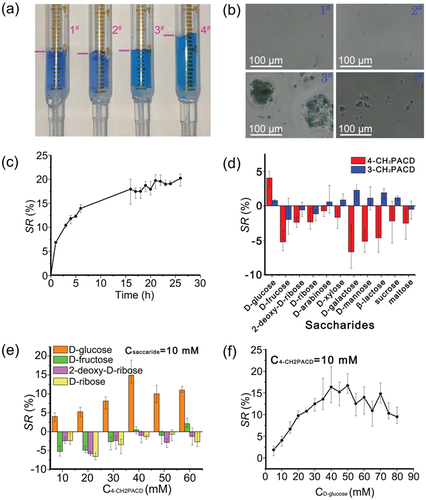
Fig. 2 response of hydrogel. A) a hydrogel with no CD derivative in the PBS solution (1#) and glucose solution (40 mm) (2#), and a picture of the gel -4PACD-10 (PBS) balanced in PBS solution (3#) and glucose solution (40 mm). B) micrographs of hydrogels, 4-CH2PACD doped into hydrogels, and aggregated as a glucose receptor with a diameter of about 100. μ M particles (3#), and when the hydrogel is immersed in glucose solution (4#), the particles decompose. C) the swelling rate of gel -4PACD-10 in the glucose solution (40 mm) along the equilibration time (SR). d) SR of gel-4pacd - in monosaccharide solution. e) SR of gel-4pacd-10 and gel-3pacd-10 in various sugar solutions. F) the SR of the gel 4PACD-10 is balanced in various concentrations of glucose solution.
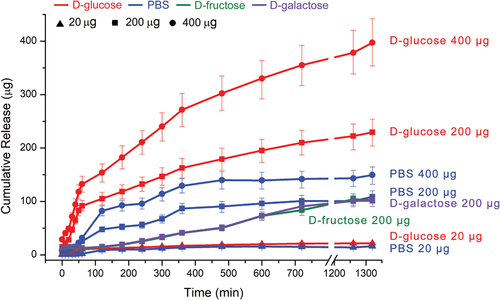
Fig. 3 loading different amounts of insulin (20, 200, 400) into PBS, D-glucose, D-fructose or D-galactose solutions respectively μ g) And balance the insulin release of gel-4pacd-10 (1 ml).
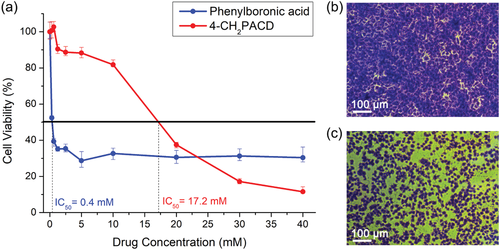
Fig. 4 evaluation of cytotoxicity of phenylboric acid and 4-ch2pacd by MTT method. The cell viability was evaluated under different concentrations of phenylboric acid and 4-ch2pacd (a). Images of cells cultured in MEM containing 10 mm 4-ch2pacd (b) and 10 mm phenylboric acid (c). Living cells are stained blue with crystal violet for visualization.
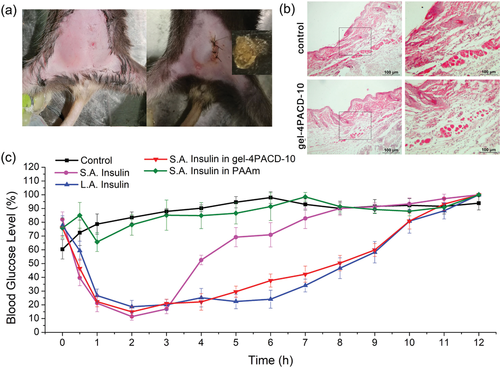
Fig. 5 the efficacy of intraperitoneal injection of insulin or intraperitoneal insulin preloading hydrogel.
[summary]
Bidentate β- CD is easily synthesized from DM by three simple reactions β CD and P (bromomethyl) phenylboronic acid. Bidentate β- The process of CD formation was found to be size selective because bidentate structure could not be provided from m (bromomethyl) phenylboronic acid β- CD derivatives. Bidentate β- CD (i.e. 4-ch2pacd) contains glucose slits and shows highly specific binding with D-glucose. The synthesized 4-CH2PACD was doped into PAAm hydrogel, giving hydrogel specific reaction to D- glucose. Specifically, when the gel is balanced in D- glucose solution, the expansion of the hydrogel is visible, while it shrinks in the D- glucose isomer (such as D- fructose and D- galactose) solution. This characteristic is found to be beneficial to self regulation of specific glucose responsive insulin release, because high concentration of D- glucose in the solution causes gel expansion and increases mesh size. In vivo test showed that the double teeth were preloaded in T1DM β- CD and short active insulin PAAm hydrogels can achieve long-term sustained glycemic control. It is expected that this simple synthetic method will be bidentate β- As the receptor of various important biological compounds or metabolites, CD opens a new door to synthesis. in consideration of β- CD is a multifunctional host guest compound with many biological or pharmaceutical active compounds, as well as bidentate β- The specific interaction between Cd and targeted biomolecules has developed a new mechanism for dsgtir.
This information is from the Internet for academic exchange only. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it immediately
18915694570
Previous: Academician He Chaolia


