Xian Jiaotong University AFM: New hydrogel wound dressings make progress in the treatment of diabetic chronic wounds
In recent years, the research on diabetic chronic wound excipients has become a difficult problem in the field of clinical treatment of diabetes. Traditional wound dressings lack the corresponding biological functions and are difficult to replace, and cannot effectively protect the wound. It is easy to cause local oxidative stress, vascular damage and secondary infections in the wound, resulting in prolonged healing. Therefore, it is extremely urgent to develop a new type of wound dressing with mechanical functions and multiple biological functions similar to skin tissue.

Recently, the research group of Cheng Yilong, a distinguished researcher of the School of Chemistry of Xi’an Jiaotong University, and the research group of Professor Li Ang of the Stomatological Hospital have successfully developed a new type of hydrogel wound dressing based on tea polyphenols (epigallocatechin gallate, EGCG) is constructed with phenylboronic acid complex, through free radical copolymerization of the dynamic crosslinking agent formed by EGCG and 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid (APBA) with acrylamide to achieve efficient and safe treatment of diabetic chronic wounds, which has important clinical significance Value.
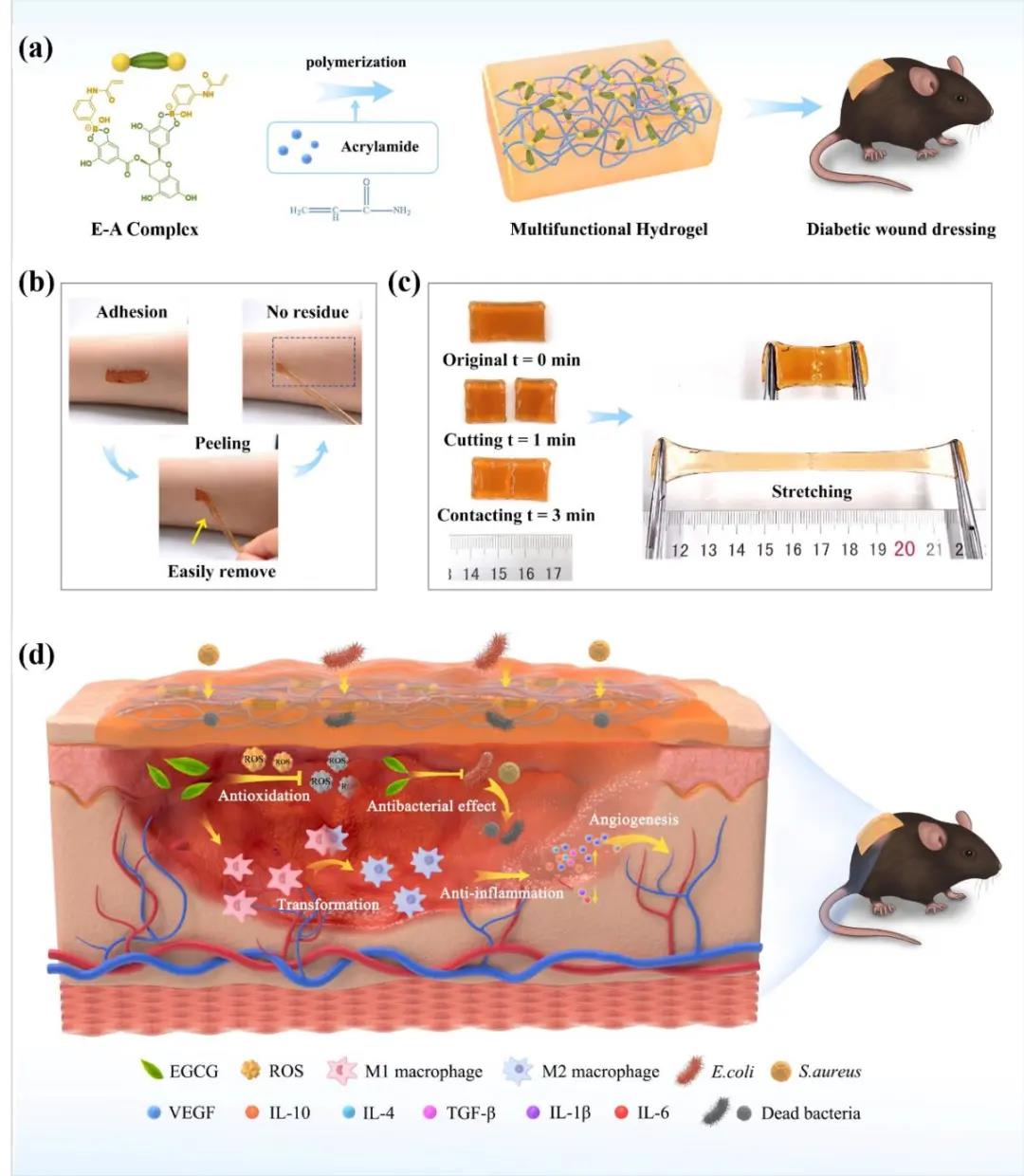
(A) Schematic diagram of material design and synthesis of hydrogel
(B) Adhesion performance photo of hydrogel
(C) Photos of self-healing properties of hydrogel
(D) Schematic diagram of the biological efficacy of hydrogel
The new hydrogel wound dressing developed by the research group has the following advantages: First, it has excellent mechanical properties and rapid self-repair function. By introducing dynamic phenylborate bonds, it can effectively avoid secondary infections caused by local body movement and dressing rupture; second, it has good tissue adhesion, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant functions. Compared with commercial dressing films, the introduction of EGCG hydrogel system can significantly accelerate wound closure, promote anti-inflammatory factors (IL-4, IL-10), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor (TGF-β) ) Expression, accelerate the transformation of macrophages M1-M2 in the wound area, and inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory factors IL-1β and IL-6. The third is to greatly improve the convenience of dressing replacement to avoid secondary wounds. With the release of EGCG, the adhesiveness of the gel system decreases and the dressing can be easily removed. At present, the research team is accelerating the application and exploration of this new hydrogel wound dressing in diabetic oral mucosal wound repair.
The research results were published in the form of papers on Advanced Functional Materials (impact factor 16.8), an authoritative journal in the international materials field. Xiaodan Zhao, a doctoral student at the Hospital of Stomatology, Dandan Pei, an associate researcher at the Hospital of Stomatology, is the co-first author of this paper. Cheng Yilong, a distinguished researcher from the School of Chemistry at Xian Jiaotong University, and Professor Li Ang from the Stomatological Hospital are the co-corresponding authors. Xi'an Jiaotong University is the first author unit and the only corresponding author unit of this article.
This research work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the basic scientific research business fees of central universities, the Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Craniomaxillofacial Precision Medicine, and the "Young Top Talent Support Program" of Xian Jiaotong University. The characterization and testing of the paper is strongly supported by the Analysis and Testing Sharing Center of Xian Jiaotong University.
Source: Xian Jiaotong University, New Materials Information
Paper link:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adfm.202009442
Homepage of Professor Li Ang: http://gr.xjtu.edu.cn/en/web/drliang/
Homepage of Researcher Cheng Yilong: http://gr.xjtu.edu.cn/en/web/yilongcheng

Recently, the research group of Cheng Yilong, a distinguished researcher of the School of Chemistry of Xi’an Jiaotong University, and the research group of Professor Li Ang of the Stomatological Hospital have successfully developed a new type of hydrogel wound dressing based on tea polyphenols (epigallocatechin gallate, EGCG) is constructed with phenylboronic acid complex, through free radical copolymerization of the dynamic crosslinking agent formed by EGCG and 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid (APBA) with acrylamide to achieve efficient and safe treatment of diabetic chronic wounds, which has important clinical significance Value.

(A) Schematic diagram of material design and synthesis of hydrogel
(B) Adhesion performance photo of hydrogel
(C) Photos of self-healing properties of hydrogel
(D) Schematic diagram of the biological efficacy of hydrogel
The new hydrogel wound dressing developed by the research group has the following advantages: First, it has excellent mechanical properties and rapid self-repair function. By introducing dynamic phenylborate bonds, it can effectively avoid secondary infections caused by local body movement and dressing rupture; second, it has good tissue adhesion, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant functions. Compared with commercial dressing films, the introduction of EGCG hydrogel system can significantly accelerate wound closure, promote anti-inflammatory factors (IL-4, IL-10), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor (TGF-β) ) Expression, accelerate the transformation of macrophages M1-M2 in the wound area, and inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory factors IL-1β and IL-6. The third is to greatly improve the convenience of dressing replacement to avoid secondary wounds. With the release of EGCG, the adhesiveness of the gel system decreases and the dressing can be easily removed. At present, the research team is accelerating the application and exploration of this new hydrogel wound dressing in diabetic oral mucosal wound repair.
The research results were published in the form of papers on Advanced Functional Materials (impact factor 16.8), an authoritative journal in the international materials field. Xiaodan Zhao, a doctoral student at the Hospital of Stomatology, Dandan Pei, an associate researcher at the Hospital of Stomatology, is the co-first author of this paper. Cheng Yilong, a distinguished researcher from the School of Chemistry at Xian Jiaotong University, and Professor Li Ang from the Stomatological Hospital are the co-corresponding authors. Xi'an Jiaotong University is the first author unit and the only corresponding author unit of this article.
This research work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the basic scientific research business fees of central universities, the Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Craniomaxillofacial Precision Medicine, and the "Young Top Talent Support Program" of Xian Jiaotong University. The characterization and testing of the paper is strongly supported by the Analysis and Testing Sharing Center of Xian Jiaotong University.
Source: Xian Jiaotong University, New Materials Information
Paper link:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adfm.202009442
Homepage of Professor Li Ang: http://gr.xjtu.edu.cn/en/web/drliang/
Homepage of Researcher Cheng Yilong: http://gr.xjtu.edu.cn/en/web/yilongcheng
18915694570
Previous: Qu Xiaogang/Ren Jinson


